Propiedades térmicas#
En el tema dedicado a la espectroscopia se han discutido las diferentes escalas energéticas asociadas a los diferentes procesos moleculares (o del sólido). Estas escalas son muy importantes para poder entender las propiedades térmicas de la materia, ya que necesitamos estudiar fenómenos cuya energía característica sea similar a la energía térmica, \(k_BT\). Dentro de un sólido tenemos procesos electrónicos y vibracionales:
En los procesos electrónicos la energía característica es el electronvoltio. Para que la energía térmica sea equiparable a un electronvoltio necesitamos temperaturas del orden de \(10^4 K\) lo cual está muy lejos del rango habitual al que se encuentra la materia.
Por otro lado, en los procesos vibracionales, la energía característica son los cientos de cm\(^{-1}\) (100cm\(^{-1}\approx 0.01\)eV) que, traducidos a una temperatura característica obtenemos, \(T \approx 140K\), con lo que a temperatura ambiente esperamos tener excitación vibracional no despreciable.
Dentro de un sólido existen otros fenómenos que operan en este rango de energía, como pueden ser los movimientos electrónicos en metales o el magnetismo. Dado que ambos fenómenos se deben de tratar bajo una teoría cuántica de la estructura electrónica de los sólidos no los discutiremos en este curso.
Ley de Dulong-Petit#
Dado que, bajo la aproximación armónica, podemos considerar las vibraciones de un sólido como partículas independientes podemos calcular su calor específico como si de un gas se tratara,
En la figura Fig. 253 podemos ver que esta aproximación funciona muy bien tanto en metales como en aislantes a alta temperatura.
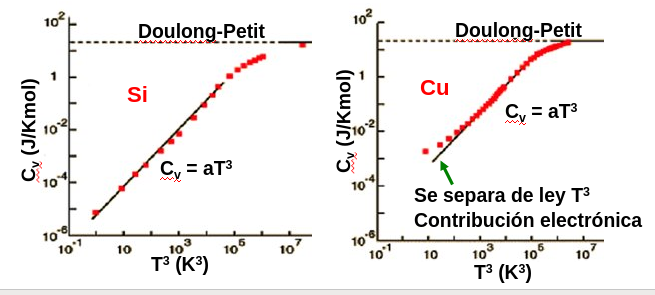
Fig. 253 Gráfica del calor específico de dos solidos, silicio y cobre. En la gráfica del silicio, a la izquierda, podemos observar como en los aislantes a alta temperatura el calor específico tiende, a alta temperatura, al límite impuesto por la ley de Dulong y Petit y, a baja temperatura, tiene un comportamiento como \(T^3\). En cambio, en los metales como el cobre (a la derecha), podemos ver que, aunque a alta temperatura se respecta la ley de Dulong y Petit a baja temperatura el calor específico varía linealmente con la temperatura.#
En la Fig. 253 podemos también observar que en aislantes, como el silicio, el calor específico decae de forma proporcional a la temperatura al cubo, \(T^3\), mientras que esto no es válido en metales, donde, a baja temperatura, \(C_v\) es lineal. Este comportamiento en \(T^3\) es el característico de las vibraciones en sólidos tridimiensionales.
Modelo Einstein#
Veamos ahora un modelo sencillo que permite justificar la ley de Dulong-Petit. Este es el modelo de Einstein para las vibraciones en los sólidos. En él se construye la energía de un cristal vibrando suponiendo que está formado por \(N\) osciladores, cada uno de frecuencia \(\omega_{a\vec{k}}\):
Es importante darse cuenta de que esta expresión no incluye la energía del punto cero ya que Einstein en el momento de formular el modelo no la conocía.
Seguidamente se realiza una aproximación suponiendo que la frecuencia de todos los modos es muy similar, \(\omega_{a\vec{k}}\approx \hbar \omega\). Con ello tenemos que la energía interna del cristal es, aproximadamente,
Con esto podemos intentar calcular tanto la capacidad específica de alta (\(KT\gg \hbar\omega\)) como de baja temperatura (\(KT\ll \hbar\omega\)),
Como podemos ver, esta sencilla expresión permite recuperar la ley empírica de Dulong y Petit, pero no predice correctamente la dependencia de la energía a baja temperatura (predice un comportamiento en \(T^{-2}\) en vez de \(T^{-3}\)). Esto se debe a la aproximación realizada anteriormente. Debye, eliminando esta condición, formuló su ley \(T^3\) que reproduce, de forma adecuada, las medidas como las que se muestran en la Fig. 253.
