Divergence¶
Definición¶
The divergence is an operator that is applied on a vector field.
(65)¶\[\vec{\nabla}\cdot \vec{f}=\frac{\partial f_x}{\partial x}+\frac{\partial f_y}{\partial y}+\frac{\partial f_z}{\partial z}\]
As can be seen, the result of the applying the divergence is a scalar field.
Interpretation¶
The divergence measures the difference between the number of field lines that enter and leave from/to a particular point.
Ejemplo
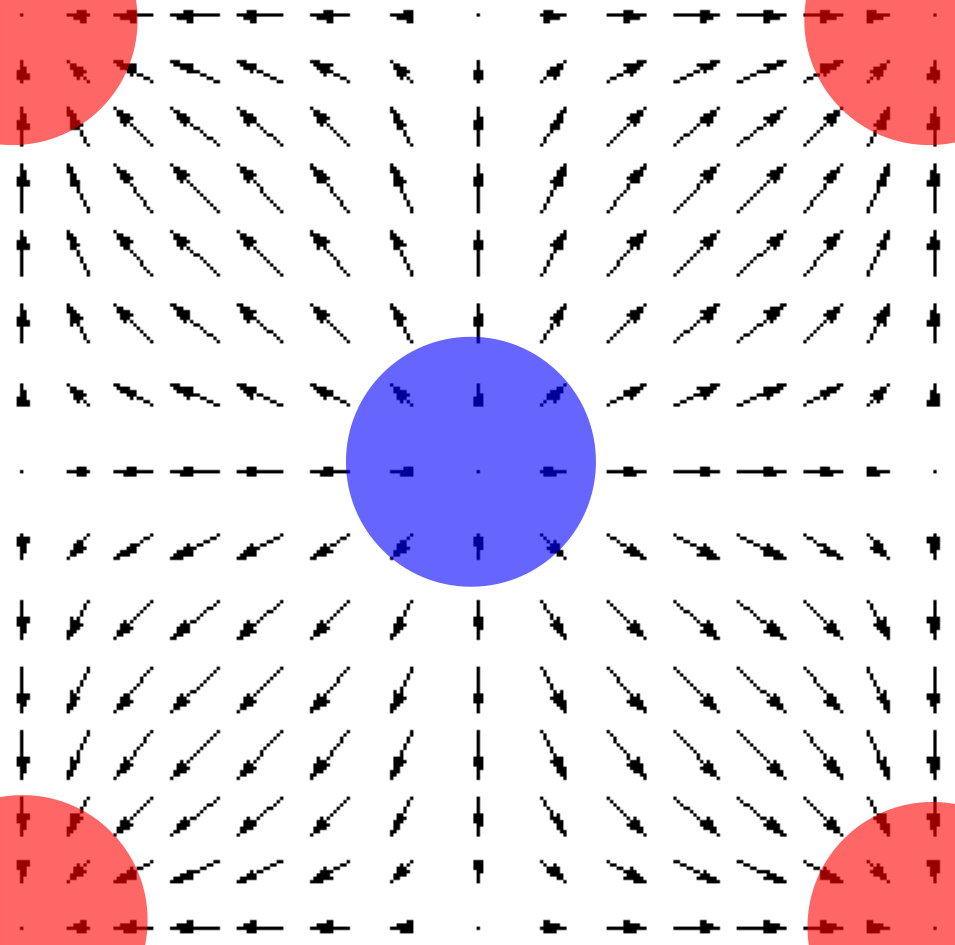
Fig. 27 The divergence measures the number of lines entering/exiting a point.¶
A positive divergence is associated with a majority of lines coming out (leaving) from a point. This point is a source of field lines. On the other hand, a point with a negative divergence is seen to come from a majority of lines entering into a point. This point is called a sink of field line.