AJAX, XML y JSON
Comunicación síncrona web
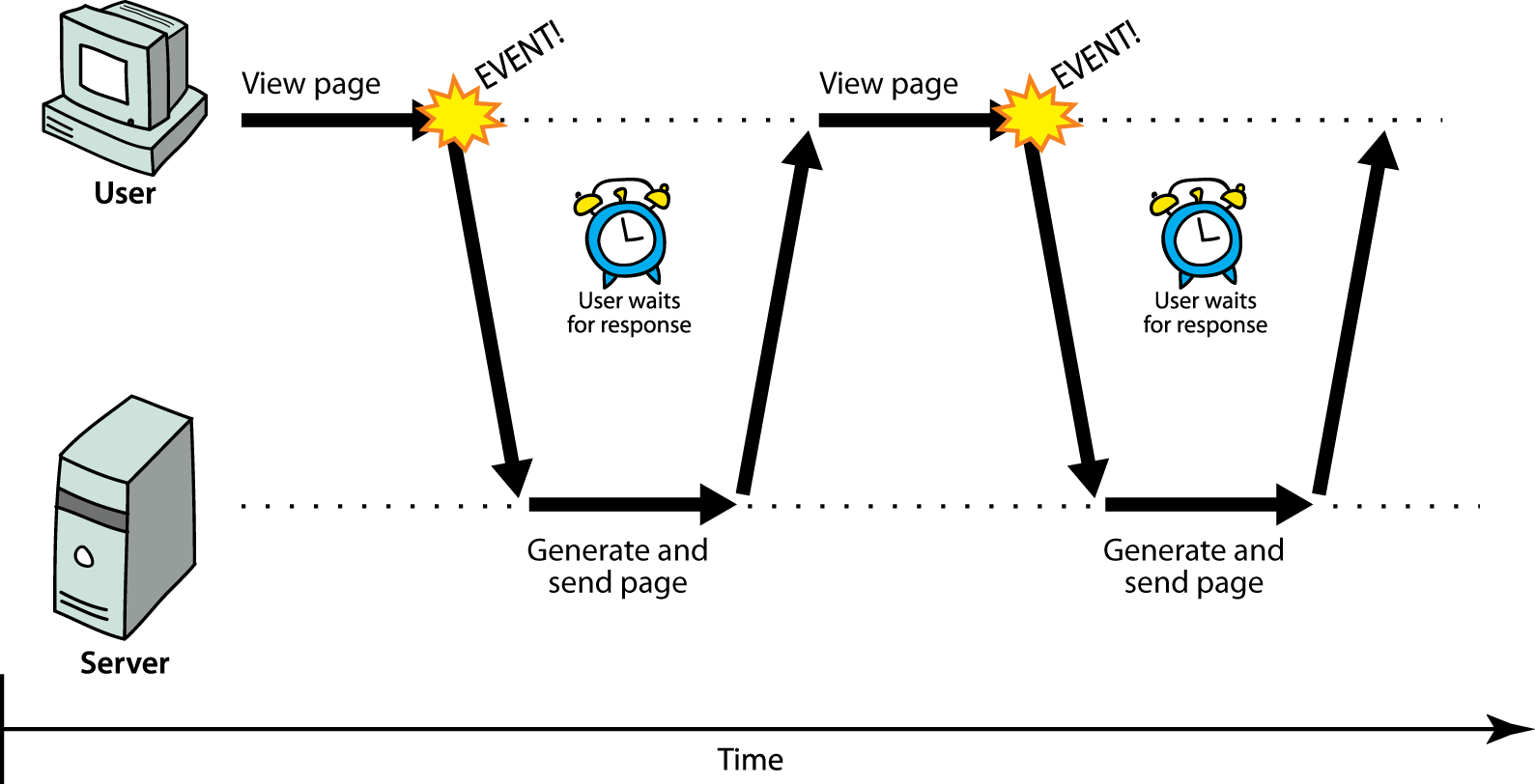
- síncrono: el usuario debe esperar mientras se cargan las nuevas páginas
- patrón de comunicación típica usado en las páginas web (click, esperar, refrescar)
Aplicaciones Web y Ajax

-
aplicación web: sitio web dinámicos que imita el comportamiento de una aplicación de escritorio
- presenta una experiencia de usuario continua en lugar de páginas páginas separadas
- ejemplos: Gmail, Google Maps, Google Docs and Spreadsheets, Flickr, A9
-
Ajax: Asynchronous JavaScript and XML
- no es un lenguaje de programación; sino una forma particular de usar JavaScript
- descarga datos desde un servidor sin interferir (detrás)
- permite la actualización dinámica de una página sin hacer esperar al usuario
- evita el patrón "click-wait-refresh"
- ejemplos: UW's CSE 14x Diff Tool, Practice-It; Google Suggest
Comunicación asíncrona web
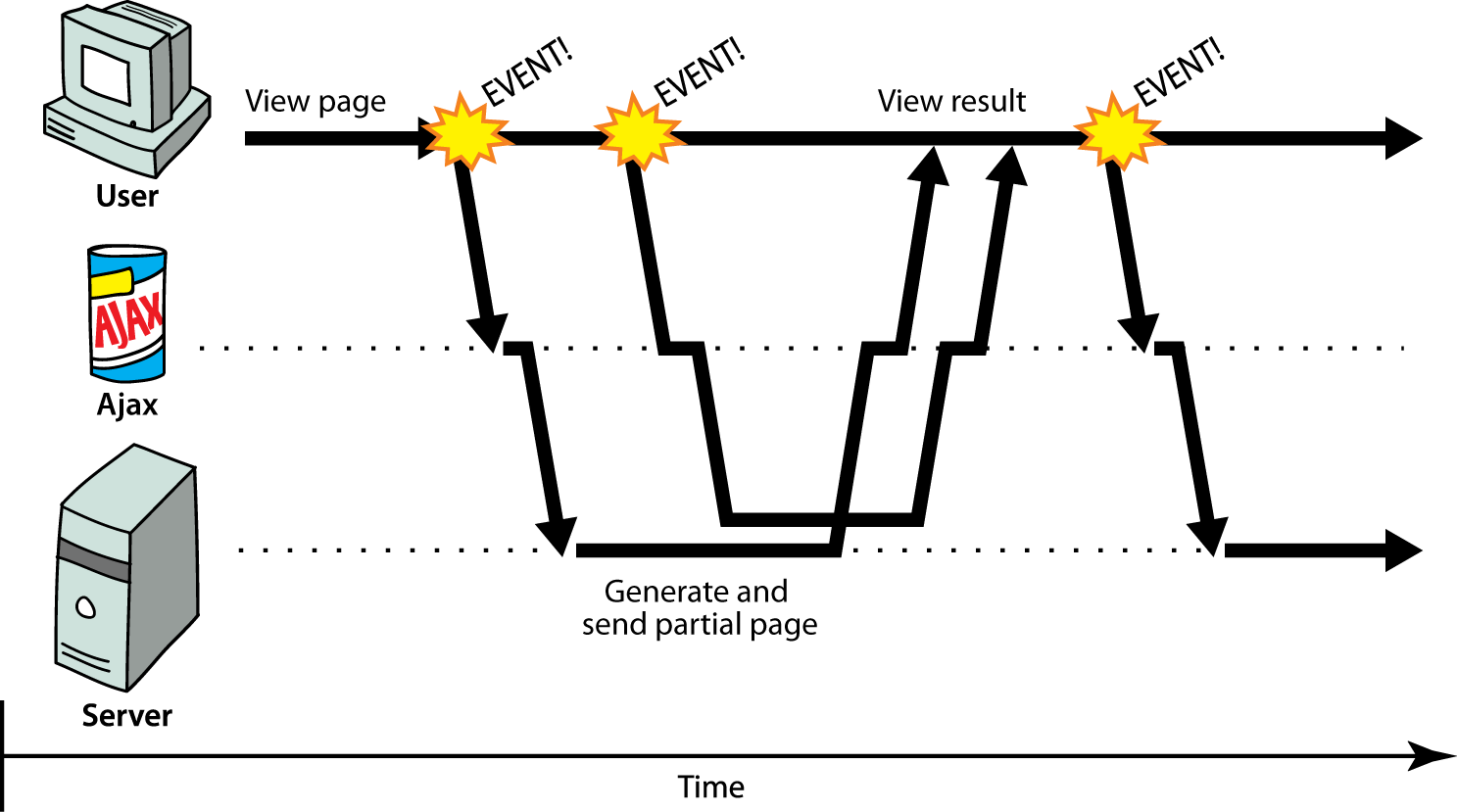
- asíncrono: el usuario puede mantener la interacción con la página
mientras se cargan los datos
- patrón de comunicación hecho posible gracias a Ajax
XMLHttpRequest
- JavaScript incluye un objeto
XMLHttpRequestque puede buscar ficheros desde el servidor. - lo puede hacer de forma asíncrona (en segundo plano, transparente al usuario)
- el contenido del fichero buscado se puede poner en la página web en curso usando DOM
Petición típica Ajax
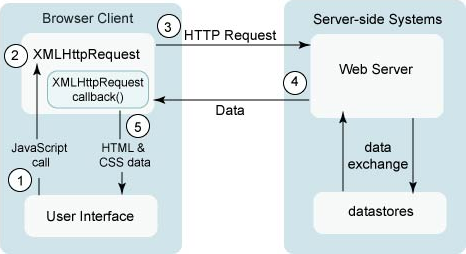
- user clicks, invoking an event handler
- handler's code creates an
XMLHttpRequestobject XMLHttpRequestobject requests page from server- server retrieves appropriate data, sends it back
XMLHttpRequestfires an event when data arrives- this is often called a callback
- you can attach a handler function to this event
- your callback event handler processes the data and displays it
Ajax - Asynchronous JavaScript and XML
Uso de Javascript para obtener más contenido desde el servidor sin navegar a otra página
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open(method, url, [async/sync]);
xhr.onload = function() { /* handle success */ };
xhr.onerror = function() { /* handle failure */ };
xhr.send();
let xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
xhr.open("GET", "data.txt");
xhr.onload = function() { alert(this.responseText); };
xhr.onerror = function() { alert("ERROR!"); };
xhr.send();
Como se ha mencionado antes no se aconseja usar el método de llamada AJAX de XML sobre HTML
jQuery's ajax method
$.ajax({
"url": "http://foo.com",
"option" : "value",
"option" : "value",
...
"option" : "value"
});
- call the
$.ajax()method - constructor accepts an object literal full of options that dictate the behavior of the AJAX request:
- the
urlto fetch, as a String, - the
typeof the request, GET or POST - etc...
- the
- hides icky details of the raw
XMLHttpRequest; works well in all browsers
$.ajax() options
| option | description |
|---|---|
url |
The URL to make a request from |
type |
whether to use POST or GET |
data |
an object literal filled with query parameters and their values |
dataType |
The type of data you are expecting to recieve, one of: "text", "html", "json", "xml" |
timeout |
an amount of time in seconds to wait for the server before giving up |
success |
event: called when the request finishes successfully |
error |
event: called when the request fails |
complete |
event: called when the request finishes successfully or erroneously |
jQuery AJAX example
$.ajax({
"url": "foo/bar/mydata.txt",
"type": "GET",
"success": myAjaxSuccessFunction,
"error": ajaxFailure
});
function myAjaxSuccessFunction(data) {
// do something with the data
}
function ajaxFailure(xhr, status, exception) {
console.log(xhr, status, exception);
}
- attach an event handler function to the request's
successanderrorevents
AJAX data parameter
The data passed to your success handler will be in whatever format you specified in the dataType option
- a
dataTypeof text returns raw text no matter its apparent data type - a
dataTypeof html returns raw html text - a
dataTypeof xml returns an XML document object - a
dataTypeof json returns a JSON object
Handling Ajax errors
$.ajax(
"url": "http://foo.com",
"type": "GET",
"success": functionName,
"error": ajaxFailure
});
...
function ajaxFailure(xhr, status, exception) {
console.log(xhr, status, exception);
}
- for user's (and developer's) benefit, show an error message if a request fails
Better jQuery AJAX
Rather than specify all of the options in an object literal...
$.ajax({
"url": "http://foo.com",
"type": "GET",
"success": functionName,
"error": ajaxFailure
});
one can pass the URL as the first parameter and the rest as an object literal.
$.ajax("http://foo.com", {
"type": "GET",
"success": functionName,
"error": ajaxFailure
});
Why? It makes it even easier to see what this AJAX request is doing.
Debugging AJAX code
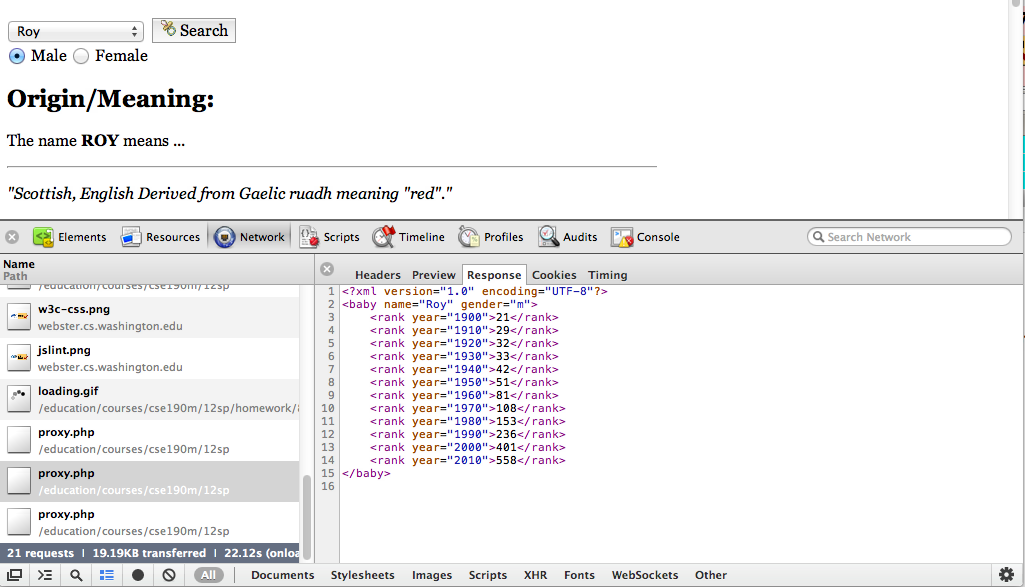
- Chrome Dev Tool's Network tab shows each request, parameters, response, errors
- expand a request by clicking on it and look at Response tab to see Ajax result
- check the Console tab for any errors that are thrown by requests
More about $.get() and $.post()
| function | description |
|---|---|
$.ajax() |
A general function for making AJAX requests, other AJAX functions rely on this |
$.get() |
makes a GET request via AJAX |
$.post() |
makes a POST request via AJAX |
Why bother making the distinction if it all boils down to a call to $.ajax() under the hood
- it is less error prone
- it is easier to read
- let's you forget about some of the AJAX options
XMLHttpRequest security restrictions
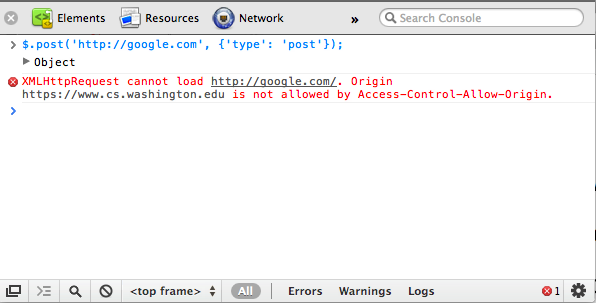
- Ajax must be run on a web page stored on a web server
- (cannot be run from a web page stored on your hard drive)
- Ajax can only fetch files from the same server that the page is on
http://www.foo.com/a/b/c.htmlcan only fetch fromwww.foo.com
XML
Storing structured data in arbitrary text formats (bad)
My note: BEGIN TO: Alice Smith (alice@example.com) FROM: Robert Jones (roberto@example.com) SUBJECT: Tomorrow's "Birthday Bash" event! MESSAGE (english): Hey Bob, Don't forget to call me this weekend! PRIVATE: true END
- Many apps make up their own custom text format for storing structured data.
- We could also send a file like this from the server to browser with Ajax.
- What's wrong with this approach?
XML: A better way of storing data
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <note private="true"> <to>Alice Smith (alice@example.com)</to> <from>Robert Jones (roberto@example.com)</from> <subject>Tomorrow's "Birthday Bash" event!</subject> <message language="english"> Hey Bob, Don't forget to call me this weekend! </message> </note>
- eXtensible Markup Language (XML) is a format for storing nested data with tags and attributes
- essentially, it's HTML, but you can make up any tags and attributes you want
- lots of existing data on the web is stored in XML format
What is XML?
- XML is a "skeleton" for creating markup languages
- you decide on an XML "language" of tags and attributes that you want to allow in your app
- XML syntax is mostly identical to HTML's:
<element attribute="value">content</element> - the HTML/XML tag syntax is a nice general syntax for describing hierarchical (nested) data
- when you choose to store data in XML format (or access external XML data), you must decide:
- names of tags in HTML:
h1,div,img, etc. - names of attributes in HTML:
id/class,src,href, etc. - rules about how they go together in HTML: inline vs. block-level elements
- names of tags in HTML:
- XML presents complex data in a human-readable, "self-describing" form
Anatomy of an XML file
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!-- XML prolog --> <note private="true"> <!-- root element --> <to>Alice Smith (alice@example.com)</to> <from>Robert Jones (roberto@example.com)</from> <subject>Tomorrow's "Birthday Bash" event!</subject> <message language="english"> Hey Bob, Don't forget to call me this weekend! </message> </note>
- begins with an
<?xml ... ?>header tag (prolog) - has a single root element (in this case,
note) - tag, attribute, and comment syntax is just like HTML
Uses of XML
- XML data comes from many sources on the web:
- web servers store data as XML files
- databases sometimes return query results as XML
- web services use XML to communicate
- XML is the de facto universal format for exchange of data
- XML languages are used for music, math, vector graphics
- popular use: RSS for news feeds & podcasts
What tags are legal in XML?
<measure number="1"> <attributes> <divisions>1</divisions> <key><fifths>0</fifths></key> <time><beats>4</beats></time> <clef> <sign>G</sign><line>2</line> </clef> </attributes> <note> <pitch> <step>C</step> <octave>4</octave> </pitch> <duration>4</duration> <type>whole</type> </note> </measure>
- any tags you want! examples:
- a library might use tags
book,title,author - a song might use tags
key,pitch,note
- a library might use tags
- when designing XML data, you choose how to best represent the data
- large or complex pieces of data become tags
- smaller details and metadata with simple types (integer, string, boolean) become attributes
XML and Ajax

- web browsers can display XML files, but often you instead want to fetch one and analyze its data
-
the XML data is fetched, processed, and displayed using Ajax
- (XML is the "X" in "Ajax")
- It would be very clunky to examine a complex XML structure as just a giant string!
- luckily, the browser can break apart (parse) XML data into a set of objects
- there is an XML DOM, similar to the HTML DOM
Fetching XML using Ajax (template)
$.get("foo.xml")
.done(functionName);
function functionName(xmlDom) {
// do stuff with the xmlDom just like you would with the HTML dom
}
- your event handler is passed an XML DOM object as a parameter
xmlDomis the XML equivalent ofdocumentin the HTML DOM, it is not the root tag
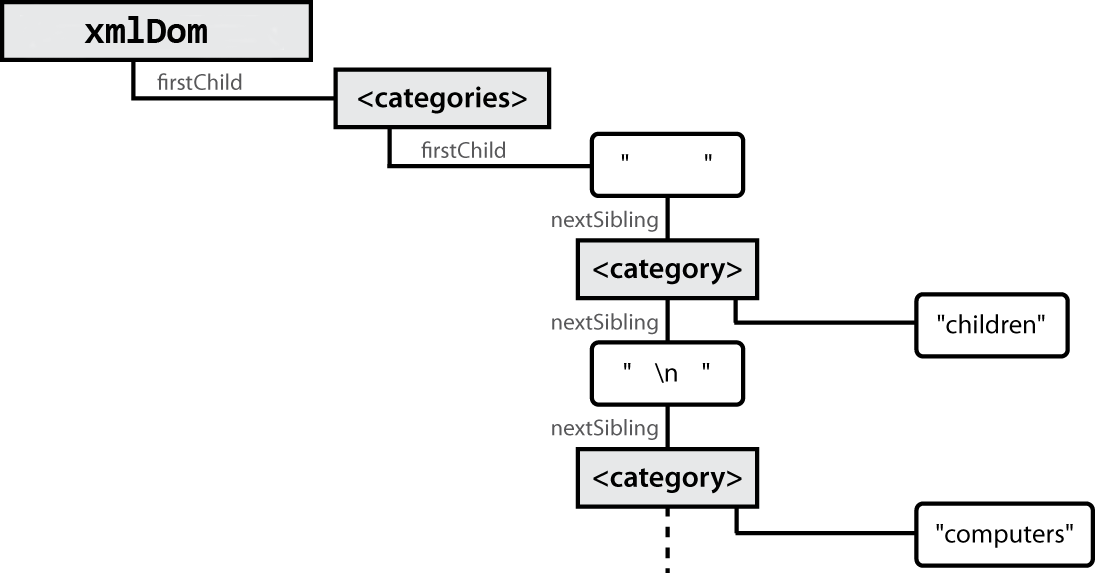
XML DOM tree structure

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <categories> <category>children</category> <category>computers</category> ... </categories>
- the XML tags have a tree structure
- DOM nodes have parents, children, and siblings
- each DOM node object has properties/methods for accessing nearby nodes
Interacting with XML DOM nodes manually

To get a list of all nodes that use a given element:
var elms = node.getElementsByTagName("tag");
To get the text inside of a node:
var text = node.firstChild.nodeValue;
To get an attribute's value from a node:
var attrValue = node.getAttribute("name");
Full list of XML DOM properties
- properties:
nodeName,nodeType,nodeValue,attributesfirstChild,lastChild,childNodes,nextSibling,previousSibling,parentNode
- methods:
getElementsByTagName,getAttribute,hasAttribute[s],hasChildNodesappendChild,insertBefore,removeChild,replaceChild
XML DOM and jQuery
You use the same jQuery functions to interact with the XML DOM, with one minor tweak:
- Identifying a node, be careful with your CSS selectors, a lot of them do not make
sense and will not work when dealing with general XML
$(xmlDom).find("tagName"); // You can use complicated CSS selectors $(xmlDom).find("ingredient[quantity='5']"); - Traversing the XML DOM
$(xmlDom).find("tagName") .parent() .children() .each(function); - Reading attributes and the text inside of an XML node
$(xmlDom).find("directions") .attr("time", "0") .text("make the dish :P");
Ajax XML DOM example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <employees> <lawyer money="99999.00" /> <janitor name="Ed"> <vacuum model="Hoover" /> </janitor> <janitor name="Bill">no vacuum, too poor</janitor> </employees>
// how much money does the lawyer make? $(xmlDom).find("lawyer").attr("money"); // "99999.00" // array of 2 janitors var janitors = $(xmlDom).find("janitor"); janitors.find("vacuum").attr("model"); // "Hoover" janitors.last().text(); // "no vacuum, too poor"
- How would we find out the first janitor's name?
- How would we find out how many janitors there are?
- How would we find out how many janitors have vs. don't have vacuums?
Larger XML file example
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <bookstore> <book category="cooking"> <title lang="en">Everyday Italian</title> <author>Giada De Laurentiis</author> <year>2005</year><price>30.00</price> </book> <book category="computers"> <title lang="en">XQuery Kick Start</title> <author>James McGovern</author> <year>2003</year><price>49.99</price> </book> <book category="children"> <title lang="en">Harry Potter</title> <author>J K. Rowling</author> <year>2005</year><price>29.99</price> </book> <book category="computers"> <title lang="en">Learning XML</title> <author>Erik T. Ray</author> <year>2003</year><price>39.95</price> </book> </bookstore>
Navigating node tree example
// make a paragraph for each book about computers $(xmlDom).find("book[category='computer']").each(function(idx, e) { // extract data from XML var title = $(e).find("title").text(); var author = $(e).find("author").text(); // make an HTML <p> tag containing data from XML $("<p>") .text(title + ", by " + author) .appendTo($(document.body)); });
JSON
JavaScript Object Notation (JSON)


JavaScript Object Notation (JSON): Data format that represents data as a set of JavaScript objects
- invented by JS guru Douglas Crockford of Yahoo!
- natively supported by all modern browsers (and libraries to support it in old ones)
- not yet as popular as XML, but steadily rising due to its simplicity and ease of use
Recall: JavaScript object syntax
var person = {
"name": "Philip J. Fry", // string
"age": 23, // number
"weight": 172.5, // number
"friends": ["Farnsworth", "Hermes", "Zoidberg"], // array
"getBeloved": function() { return this.name + " loves Leela"; }
};
alert(person.age); // 23
alert(person["weight"]); // 172.5
alert(person.friends[2])); // Zoidberg
alert(person.getBeloved()); // Philip J. Fry loves Leela
- in JavaScript, you can create a new object without creating a class
- the object can have methods (function properties) that refer to itself as
this - can refer to the fields with
["fieldName"]or.fieldNamesyntax if fieldName is a legal Javascript identifier - field names can optionally be put in quotes (e.g.
weightabove)
An example of XML data
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <note private="true"> <from>Alice Smith (alice@example.com)</from> <to>Robert Jones (roberto@example.com)</to> <to>Charles Dodd (cdodd@example.com)</to> <subject>Tomorrow's "Birthday Bash" event!</subject> <message language="english"> Hey guys, don't forget to call me this weekend! </message> </note>
The equivalant JSON data
{
"private": "true",
"from": "Alice Smith (alice@example.com)",
"to": [
"Robert Jones (roberto@example.com)",
"Charles Dodd (cdodd@example.com)"
],
"subject": "Tomorrow's \"Birthday Bash\" event!",
"message": {
"language": "english",
"text": "Hey guys, don't forget to call me this weekend!"
}
}
Browser JSON methods
| method | description |
|---|---|
JSON.parse(string)
|
converts the given string of JSON data into an equivalent JavaScript object and returns it |
JSON.stringify(object)
|
converts the given object into a string of JSON data (the opposite of JSON.parse)
|
- you can use Ajax to fetch data that is in JSON format
- then call
JSON.parseon it to convert it into an object - then interact with that object as you would with any other JavaScript object
JSON expressions exercise
var data = JSON.parse(jsonString);
{
"window": {
"title": "Sample Widget",
"width": 500,
"height": 500
},
"image": {
"src": "images/logo.png",
"coords": [250, 150, 350, 400],
"alignment": "center"
},
"messages": [
{"text": "Save", "offset": [10, 30]}
{"text": "Help", "offset": [ 0, 50]},
{"text": "Quit", "offset": [30, 10]},
],
"debug": "true"
}
Given the JSON data at right, what expressions would produce:
- The window's title?
- The image's third coordinate?
- The number of messages?
- The y-offset of the last message?
var title = data.window.title; var coord = data.image.coords[2]; var len = data.messages.length; var y = data.messages[len - 1].offset[1];
JSON and AJAX (AJAJ?...)
$.get("foo.json")
.done(functionName);
function functionName(jsonObj) {
// do stuff with the jsonObj
}
- your event handler is passed a JSON object as a parameter
Referencias
- Web Programming Step by Step, 2 ed., Jessica Miller, Victoria Kirst, Marty Stepp. Lulu. 2012
- Ajax, XML, JSON
- Web de JSON
- Ejemplos
- Ejemplo ajax, fichero info.txt (servidor)
- Ejemplo ajax xml, fichero cd_catalog.xml (servidor)
- Ejemplo ajax json, fichero json_demo.txt (servidor)